Illustration
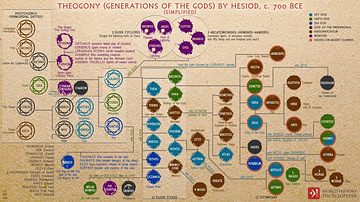
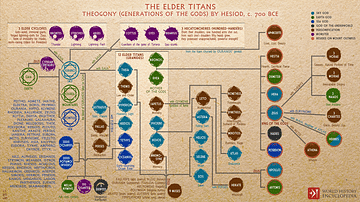
This infographic illustrates the 12 Olympian Gods (Greek: Δωδεκάθεον, Dodekatheon), the principal deities of the Greek pantheon who reside on Mount Olympus, ruling over aspects of the natural world, human life, and cosmic order. Traditionally, they include Zeus, Hera, Poseidon, Demeter, Athena, Apollo, Artemis, Ares, Aphrodite, Hephaestus, Hermes, and Dionysus, with Hades (brother of Zeus and Poseidon) excluded as he rules the underworld. The worship of these gods dates back to the Mycenaean period (c. 1600–1100 BCE), with the oldest known written mentions of the 12 Olympians appearing in the works of Homer and Hesiod around the 8th century BCE.
Variations of the 12 include Hestia instead of Dionysus and sometimes Leto, Heracles, or Asclepius.
About the Author
Cite This Work
APA Style
Netchev, S. (2024, October 01). The Twelve Olympian Gods of Ancient Greece. World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/image/19516/the-twelve-olympian-gods-of-ancient-greece/
Chicago Style
Netchev, Simeon. "The Twelve Olympian Gods of Ancient Greece." World History Encyclopedia. Last modified October 01, 2024. https://www.worldhistory.org/image/19516/the-twelve-olympian-gods-of-ancient-greece/.
MLA Style
Netchev, Simeon. "The Twelve Olympian Gods of Ancient Greece." World History Encyclopedia. World History Encyclopedia, 01 Oct 2024. Web. 19 Feb 2025.